XML data type is commonly supported in Teradata. Together with native XML type, a number of XML functions are added to support extracting values from XML, shredding and publishing JSON, etc.
infoThe following code snippets use string literal to demonstrate the usage of these functions; you can replace them with any XML column in your table.
CREATEXML function
CREATEXML is used to convert VARCHAR column to XML column.
Example:
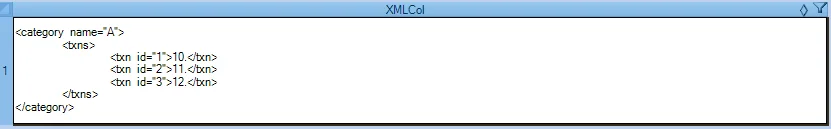
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol;
Output:
XMLExtract function
XMLEXTRACT function can be used to extract value from XML type columns.
Example:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT T.XMLCol.XMLEXTRACT('//txn[@id=3]/text()','') FROM T;
Output:
12.
XMLSERIALIZE function
XMLSerialize function can be used to convert XML type to other data types.
Example:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT XMLSerialize(CONTENT T.XMLCol.XMLEXTRACT('//txn/@id/string()','') AS VARCHAR(100)) as amount FROM T;
Output:
1 2 3
XMLQUERY function
XMLQUERY function can be used to evaluate values via XPath expression.
Example for querying XML attribute node:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT XMLQUERY('/category/@name/string()'
PASSING BY VALUE T.XMLCol
RETURNING CONTENT
EMPTY ON EMPTY
) FROM T;
Output:
A
Example for querying Element node:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT XMLQUERY('//txn[@id>=2]/string()'
PASSING BY VALUE T.XMLCol
RETURNING CONTENT
EMPTY ON EMPTY
) FROM T;
Output:
11. 12.
Another example:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT XMLQUERY('//txn[@id>=2]'
PASSING BY VALUE T.XMLCol
RETURNING CONTENT
EMPTY ON EMPTY
) FROM T;
Output:
<txn id="2">11.</txn><txn id="3">12.</txn>
For more details about XPath expressions, refer to this W3C official documentation.
XMLTABLE function
XMLTABLE function converts an XML tree structure to a row set.
Here is an example of omitting COLUMNS clause thus the items are returned as a XML column type:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT X.* FROM T,
XMLTable(
'//txn'
PASSING T.XMLCol
) AS X("ItemXml");
Output:
ItemXml
1 <txn id="1">10.</txn>
2 <txn id="2">11.</txn>
3 <txn id="3">12.</txn>
Example with COLUMNS clause:
WITH T AS
(
SELECT CREATEXML('<category name="A">
<txns>
<txn id="1" date="2020-01-01">10.</txn>
<txn id="2">11.</txn>
<txn id="3" date="2020-01-03">12.</txn>
</txns>
</category>') AS XMLCol
)
SELECT X.* FROM T,
XMLTable(
'//txn'
PASSING T.XMLCol
COLUMNS
"SeqNo" FOR ORDINALITY,
"TxnID" INT PATH '@id',
"TxnDate" DATE PATH '@date' DEFAULT DATE'9999-12-31',
"Amount" DECIMAL(20,2) PATH './text()'
) AS X(SeqNo,TxnID,TxnDate,Amount);
Output:
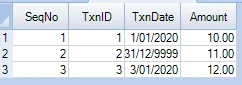
Once COLUMNS statement is added, the result is a table.
XMLAGG function
XMLAGG function can be used to convert records to XML data type.
Create a table using the following statements:
create set table TestDb.test_table
(
id int not null,
category varchar(10),
amount int
)
primary index (id);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(1,'A',10);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(2,'A',11);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(3,'A',12);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(4,'B',100);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(5,'B',101);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(6,'B',102);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(4,'C',1000);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(5,'C',1001);
insert into TestDb.test_table values(6,'C',1002);
And then use XMLAGG function to create XML column:
SELECT category, XMLAGG(XMLELEMENT (NAME "txn", XMLATTRIBUTES(id as "id"), amount)
ORDER BY id) as Transactions
FROM TestDb.test_table
group by category;
Output:
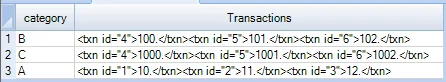
The output column Transactions is not a valid XML Document as there is no root element.
We can use XMLAGG together with XMLSERIALIZE function to create a valid XML document for each category in the table:
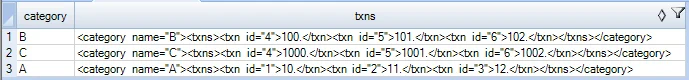
SELECT category, XMLSERIALIZE(DOCUMENT XMLDOCUMENT
(XMLELEMENT(NAME "category",
XMLATTRIBUTES(t.category as "name"),
XMLELEMENT(NAME "txns",
XMLAGG(XMLELEMENT (NAME "txn", XMLATTRIBUTES(t.id as "id"), t.amount)
ORDER BY t.id)
)
)) AS VARCHAR(200)) AS "txns"
FROM TestDb.test_table t
GROUP BY category;
Result:
Another example is to convert the whole table records to a single XML document:
SELECT XMLSERIALIZE(DOCUMENT XMLDOCUMENT
(XMLELEMENT(NAME "txns",
XMLAGG(XMLELEMENT (NAME "txn",
XMLATTRIBUTES(t1.id as "id", t1.category as "category"),
t1.amount)
ORDER BY t1.id
)
)
) AS VARCHAR(2000)) AS "txns"
FROM (SELECT 0 AS GRP, t.* FROM TestDb.test_table t) AS t1
GROUP BY t1.GRP;
Output:
<txns><txn id="1" category="A">10.</txn><txn id="2" category="A">11.</txn><txn id="3" category="A">12.</txn><txn id="4" category="B">100.</txn><txn id="4" category="C">1000.</txn><txn id="5" category="C">1001.</txn><txn id="5" category="B">101.</txn><txn id="6" category="C">1002.</txn><txn id="6" category="B">102.</txn></txns>
For the serialized type, it needs to be large enough to contain all the elements.
For XML publishing, you can also the following two procedures:
- XMLPUBLISH_STREAM
- XMLPUBLISH
Find more details on Teradata official documentation.