Spark doesn't include built-in HBase connectors. We can use HBase Spark connectoror other third party connectors to connect to HBase in Spark.
Prerequisites
If you don't have Spark or HBase available to use, you can follow these articles to configure them.
Spark
Apache Spark 3.0.1 Installation on Linux or WSL Guide
HBase
Install HBase in WSL - Pseudo-Distributed Mode
Prepare HBase table with data
Run the following commands in HBase shell to prepare a sample table that will be used in the following sections.
create 'Person', 'Name', 'Address'
put 'Person', '1', 'Name:First', 'Raymond'
put 'Person', '1', 'Name:Last', 'Tang'
put 'Person', '1', 'Address:Country', 'Australia'
put 'Person', '1', 'Address:State', 'VIC'
put 'Person', '2', 'Name:First', 'Dnomyar'
put 'Person', '2', 'Name:Last', 'Gnat'
put 'Person', '2', 'Address:Country', 'USA'
put 'Person', '2', 'Address:State', 'CA'
The table returns the following result when scanning:
scan 'Person'
ROW COLUMN+CELL
1 column=Address:Country, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:48:42.088, value=Australia
1 column=Address:State, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:48:46.750, value=VIC
1 column=Name:First, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:48:32.544, value=Raymond
1 column=Name:Last, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:48:37.085, value=Tang
2 column=Address:Country, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:49:00.692, value=USA
2 column=Address:State, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:49:04.972, value=CA
2 column=Name:First, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:48:51.653, value=Dnomyar
2 column=Name:Last, timestamp=2021-02-05T20:48:56.665, value=Gnat
2 row(s)
Build HBase Spark connector
infoIf you don't want to build the packages by yourself, please go to Summary section to directly download the binary package I built using the following approach. The built package is only provided for testing & learn purposes.
We need to build HBase Spark Connector for Spark 3.0.1 as it is not published on Maven repository.
Refer to official repo hbase-connectors/spark at master · apache/hbase-connectors for more details.
- Clone the repository using the following command:
git clone https://github.com/apache/hbase-connectors.git
- Install Maven if it is not available on your WSL:
- Change directory to the clone repo:
cd hbase-connectors/
- Build the project using the following command:
mvn -Dspark.version=3.0.1 -Dscala.version=2.12.10 -Dscala.binary.version=2.12 -Dhbase.version=2.2.4 -Dhadoop.profile=3.0 -Dhadoop-three.version=3.2.0 -DskipTests -Dcheckstyle.skip -U clean package
The version arguments need to match with your Hadoop, Spark and HBase versions.
infoFor HBase version, I have to use 2.2.4 as the latest hbase-connector code was based on that version. Otherwise the built will fail with error like this: [ERROR] ../hbase-connectors/kafka/hbase-kafka-proxy/src/main/java/org/apache/hadoop/hbase/kafka/KafkaTableForBridge.java:[53,8] org.apache.hadoop.hbase.kafka.KafkaTableForBridge is not abstract and does not override abstract method getRegionLocator() in org.apache.hadoop.hbase.client.Table Regardless of this, the built package will also work with HBase 2.4.1.
Wait until the build is completed.
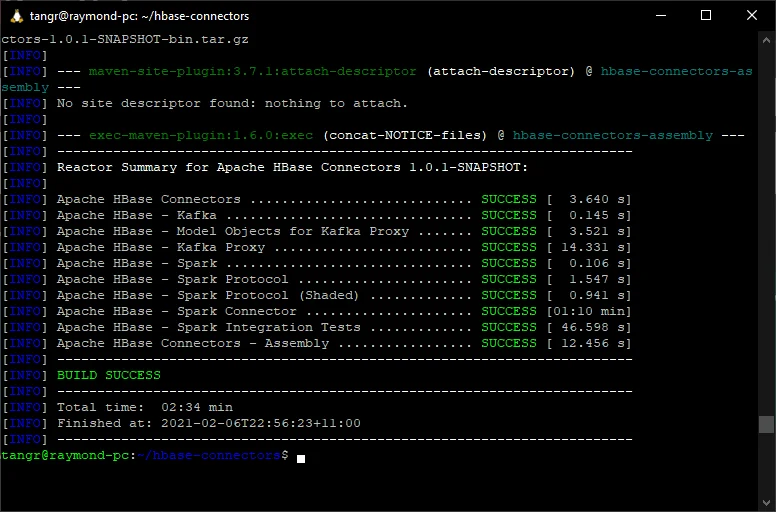
The Spark connector JAR file locates in ~/hbase-connectors/spark/hbase-spark/target/hbase-spark-1.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.
Run Spark shell
For simplicity, I will directly use Spark Shell (Scala) for this demo. You can use PySpark, Scala or other Spark supported languages to implement the logic in a script.
Start Spark-Shell with HBase connector
Start Spark Shell using the following command:
spark-shell --jars ~/hbase-connectors/spark/hbase-spark/target/hbase-spark-1.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar -c spark.ui.port=11111
Remember to change hbase-spark package to your own location.
Once Spark session is created successfully, the terminal looks like the following screenshot:
Create DataFrame
- First import the required classes:
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.spark.HBaseContext
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.HBaseConfiguration
- Create HBase configurations
val conf = HBaseConfiguration.create()
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "127.0.0.1:10231")
- Create HBase context
// Instantiate HBaseContext that will be used by the following code
new HBaseContext(spark.sparkContext, conf)
- Create DataFrame
val hbaseDF = (spark.read.format("org.apache.hadoop.hbase.spark")
.option("hbase.columns.mapping",
"rowKey STRING :key," +
"firstName STRING Name:First, lastName STRING Name:Last," +
"country STRING Address:Country, state STRING Address:State"
)
.option("hbase.table", "Person")
).load()
The columns mapping matches with the definition in the steps above.
- Show DataFrame schema
scala> hbaseDF.schema
res2: org.apache.spark.sql.types.StructType = StructType(StructField(lastName,StringType,true), StructField(country,StringType,true), StructField(state,StringType,true), StructField(firstName,StringType,true), StructField(rowKey,StringType,true))
- Show data
hbaseDF.show()
The output should look something like the following screenshot:
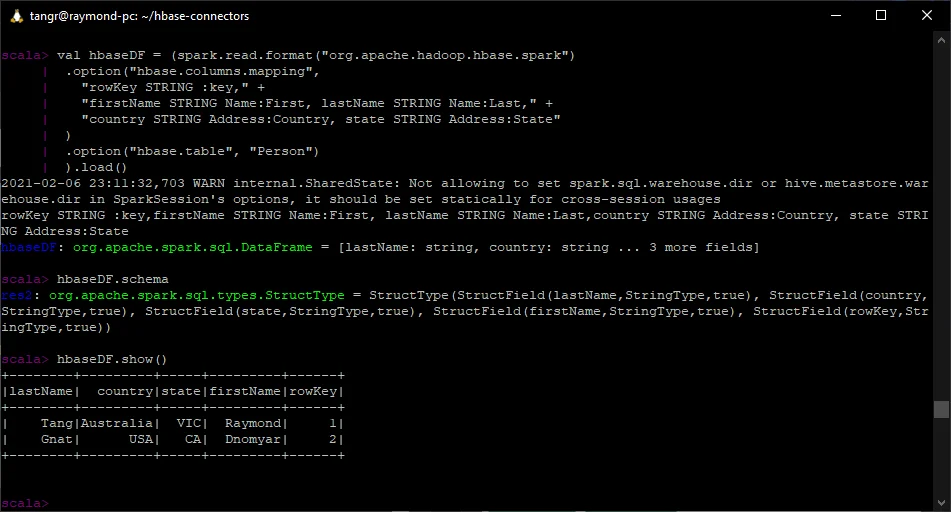
Till now, we've successfully loaded data from HBase in Spark 3.0.1.
You can also write into HBase from Spark too. Refer to the API documentation for more details.
Use catalog
We can also define a catalog for the table Person created above and then use it to read data.
- Define catalog
def catalog = s"""{
|"table":{"namespace":"default", "name":"Person"},
|"rowkey":"key",
|"columns":{
|"rowkey":{"cf":"rowkey", "col":"key", "type":"string"},
|"firstName":{"cf":"Name", "col":"First", "type":"string"},
|"lastName":{"cf":"Name", "col":"Last", "type":"string"},
|"country":{"cf":"Address", "col":"Country", "type":"string"},
|"state":{"cf":"Address", "col":"State", "type":"string"}
|}
|}""".stripMargin
- Use catalog
Now the catalog can be directly passed into as tableCatalog option:
import org.apache.hadoop.hbase.spark.datasources._
(spark.read
.options(Map(HBaseTableCatalog.tableCatalog->catalog))
.format("org.apache.hadoop.hbase.spark")
.load()).show()
The code can also be simplified as:
(spark.read.format("org.apache.hadoop.hbase.spark")
.option("catalog",catalog)
.load()).show()
Output:
scala> (spark.read
| .options(Map(HBaseTableCatalog.tableCatalog->catalog))
| .format("org.apache.hadoop.hbase.spark")
| .load()).show()
+--------+------+---------+-----+---------+
|lastName|rowkey| country|state|firstName|
+--------+------+---------+-----+---------+
| Tang| 1|Australia| VIC| Raymond|
| Gnat| 2| USA| CA| Dnomyar|
+--------+------+---------+-----+---------+
Summary
Unfortunately the connector packages for Spark 3.x are not published to Maven central repositories yet.
To save time for building hbase-connector project, you can download it from the ones I built using WSL: Release 1.0.1 HBase Connectors for Spark 3.0.1 · kontext-tech/hbase-connectors.