In this serial, I will compare Teradata SQL with T-SQL with samples provided. This is mainly prepared for SQL Server DBAs, Developers and other users to help them quickly master the common used SQLs in Teradata platform. Similar to T-SQL, Teradata SQL implements most part of the ANSI SQL with extensions. This serial is not to talk about low level architecture differences but to compare the SQL differences from a user’s perspective.
The main content I will cover in this serial are:
- Preparation
- The SELECT Statement
- Filtering and Sorting
- Combing Sets
- Grouping and Windowing
- Creating Tables
- Inserting, Updating and Deleting
- Views and Functions
- Stored Procedures
- Transaction, Error Handling and Dynamic SQL
- Indexes and Statistics
- Cursor, Sets and Temporary Tables
- Execution Plan and Performance Tuning
As a SQL Server Developer, you will find most of the statements are similar though there are some small variances.
In the post, I will only cover the first one Preparation. Please subscribe the RSS to get noticed when I post the other ones in future.
https://app.kontext.tech/Syndication/RSS/102.xml
Prerequisites
- Teradata & Teradata Studio Express
If you have no Teradata database installed, follow the instructions in my following post to setup one.
Install Teradata Express 15.0.0.8 by Using VMware Player 6.0 in Windows
I found one issue when I allocated insufficient memory to the virtual machine: the database status is: 1/5: DBS Startup - Voting for Transaction Recovery. When I allocate 2GB memory to the VM, there will be no such issue.
# pdestate -aPDE state is RUN/STARTED.DBS state is 1/5: DBS Startup - Voting for Transaction Recovery
The normal status should be:
TDExpress15.0.0.8_Sles10:~ # pdestatePDE state is RUN/STARTED.TDExpress15.0.0.8_Sles10:~ # pdestate -aPDE state is RUN/STARTED.DBS state is 4: Logons are enabled - Users are logged onTDExpress15.0.0.8_Sles10:~ #
- SQL Server 2012 and SSMS
The database version I am using is:
Microsoft SQL Server 2012 - 11.0.2218.0 (X64) Jun 12 2012 13:05:25 Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation Enterprise Edition (64-bit) on Windows NT 6.2 <X64> (Build 9200: )
Preparation – SQL Server
Run the following code in SSMS to setup the database, tables and data that will be used.
-- Create the database
CREATE DATABASE TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB;
GO
USE TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB;
GO
-- Create table Department
CREATE TABLE Department
(
DepartmentID NUMERIC(5) NOT NULL,
DepartmentName VARCHAR(10),
DepartmentManagerEmployeeID NUMERIC(5),
CONSTRAINT Department_PK PRIMARY KEY (DepartmentID)
);
GO
-- Create table Employee
CREATE TABLE Employee
(
EmployeeID NUMERIC(5) NOT NULL,
EmployeeName VARCHAR(10),
EmployeeManagerEmployeeID NUMERIC(5),
DepartmentID NUMERIC(5),
Gendar CHAR(1),
Birthday DATE,
JobGrade NUMERIC(1),
Salary NUMERIC(10,2),
CONSTRAINT Employee_PK PRIMARY KEY (EmployeeID),
CONSTRAINT Employee_FK_DepartmentID FOREIGN KEY (DepartmentID) REFERENCES Department(DepartmentID)
);
GO
-- Insert department data
INSERT INTO [Department]
([DepartmentID]
,[DepartmentName]
,[DepartmentManagerEmployeeID])
VALUES
(101 ,'HR' ,10001),
(102 ,'Risk' ,10002),
(103 ,'Sales' ,10003),
(104 ,'IT Support' ,10004),
(105 ,'Finance' ,NULL)
;
GO
-- Insert employee data
INSERT INTO [dbo].[Employee]
([EmployeeID]
,[EmployeeName]
,[EmployeeManagerEmployeeID]
,[DepartmentID]
,[Gendar]
,[Birthday]
,[JobGrade]
,[Salary])
VALUES
(10001,'Andre' ,NULL,101 ,'M','1965-02-01' ,2 , 150000),
(10002,'Lucy' ,NULL,102 ,'F','1967-03-01' ,2 ,140200),
(10003,'John' ,NULL,103 ,'M','1969-02-09' ,2 ,130900),
(10004,'Sarah' ,NULL,104 ,'F','1956-05-01' ,2 ,145000),
(10005,'Fred' ,NULL,105 ,'M','1963-02-01' ,2 ,160300),
(10006,'Freya' ,10001,101 ,'F','1985-04-01' ,2 ,110100),
(10007,'Derek' ,10006,101 ,'M','1975-02-01' ,2 ,100200),
(10008,'Nancy' ,10004,104 ,'F','1983-02-01' ,2 ,93000),
(10009,'David' ,10005,105 ,'M','1966-05-01' ,2 ,112000);
GO
Preparation – Teradata
Run the following code in Teradata Studio Express to setup the database, tables and data that will be used.
-- Create databse
CREATE DATABASE TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB
AS
PERM = 1000000
SPOOL = 2000000
FALLBACK;
-- Create table Department
CREATE TABLE TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department
(
DepartmentID NUMERIC(5) NOT NULL,
DepartmentName VARCHAR(10),
DepartmentManagerEmployeeID NUMERIC(5)
)
UNIQUE PRIMARY INDEX (DepartmentID)
;
-- Create table Employee
CREATE TABLE TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(
EmployeeID NUMERIC(5) NOT NULL,
EmployeeName VARCHAR(10),
EmployeeManagerEmployeeID NUMERIC(5),
DepartmentID NUMERIC(5),
Gendar CHAR(1),
Birthday DATE,
JobGrade NUMERIC(1),
Salary NUMERIC(10,2)
)
UNIQUE PRIMARY INDEX (EmployeeID)
INDEX (DepartmentID);
-- Insert department data
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department
(DepartmentID
,DepartmentName
,DepartmentManagerEmployeeID)
VALUES
(101 ,'HR' ,10001);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department
(DepartmentID
,DepartmentName
,DepartmentManagerEmployeeID)
VALUES
(102 ,'Risk' ,10002);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department
(DepartmentID
,DepartmentName
,DepartmentManagerEmployeeID)
VALUES
(103 ,'Sales' ,10003);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department
(DepartmentID
,DepartmentName
,DepartmentManagerEmployeeID)
VALUES
(104 ,'IT Support' ,10004);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department
(DepartmentID
,DepartmentName
,DepartmentManagerEmployeeID)
VALUES
(105 ,'Finance' ,NULL)
;
-- Insert employee data
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10001,'Andre' ,NULL,101 ,'M','1965-02-01' ,2 , 150000);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10002,'Lucy' ,NULL,102 ,'F','1967-03-01' ,2 ,140200);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10003,'John' ,NULL,103 ,'M','1969-02-09' ,2 ,130900);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10004,'Sarah' ,NULL,104 ,'F','1956-05-01' ,2 ,145000);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10005,'Fred' ,NULL,105 ,'M','1963-02-01' ,2 ,160300);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10006,'Freya' ,10001,101 ,'F','1985-04-01' ,2 ,110100);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10007,'Derek' ,10006,101 ,'M','1975-02-01' ,2 ,100200);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10008,'Nancy' ,10004,104 ,'F','1983-02-01' ,2 ,93000);
INSERT INTO TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee
(EmployeeID
,EmployeeName
,EmployeeManagerEmployeeID
,DepartmentID
,Gendar
,Birthday
,JobGrade
,Salary)
VALUES
(10009,'David' ,10005,105 ,'M','1966-05-01' ,2 ,112000);
Verify the Data
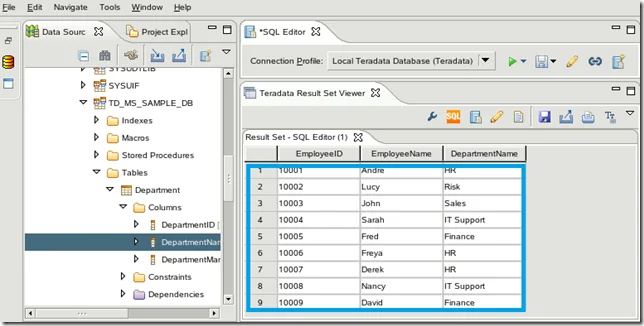
Run the following query in Teradata, you should get the same result as the screenshot:
SELECT Emp.EmployeeID,
Emp.EmployeeName,
Dept.DepartmentName
FROM TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Employee Emp
INNER JOIN TD_MS_SAMPLE_DB.Department Dept
ON Dept.DepartmentID = Emp.DepartmentID
ORDER BY Emp.EmployeeID;
Result: