Pandas is commonly used by Python users to perform data operations. In many scenarios, the results need to be saved to a storage like Teradata. This article shows you how to do that easily using JayDeBeApior sqlalchemy-teradata package.
Prerequisites
Teradata JDBC & JayDeBeApi
JayDeBeApi package and Teradata JDBC driver are required. They are commonly used in many of my articles.
For installation and more details, refer to Create, Insert, Delete, Update Operations on Teradata via JDBC in Python.
For this article, I am using TeraJDBC__indep_indep.16.20.00.13 (only one JAR file is required).
sqlalchemy-teradata
Install this package via the following command line:
pip install sqlalchemy
pip install sqlalchemy-teradata
And also make sure you have Teradata Database ODBC Driver 16.10 (or any other Teradata compatible drivers) installed on your computer too.
Teradata
If you want to setup a Teradata server on your Windows, refer to the following article:
Install Teradata Express 15.0.0.8 by Using VMware Player 6.0 in Windows
Sample data
The sample data from one of the previous examples: Python: Load / Read Multiline CSV File.
ID,Text1,Text2
1,Record 1,Hello World!
2,Record 2,Hello Hadoop!
3,Record 3,"Hello
Kontext!"
4,Record 4,Hello!
Approach 1 - JayDeBeApi
To improve performance, we use executemanyfunction so insert multiple records.
Code snippet
The following code snippet does these operations:
- Establish a JDBC connection using connect function.
- Create a cursor object
- The cursor object is then used to create a table in the database
- and insert all the records into the database via batch mode.
- Close cursor and connection. (always a good practice when connecting to database)
import jaydebeapi
import pandas as pd
file_path = 'data.csv'
pdf = pd.read_csv(file_path)
database = "TestDb"
table = "csv_jaydebeapi"
user = "dbc"
password = "dbc"
driver = 'com.teradata.jdbc.TeraDriver'
conn = jaydebeapi.connect(driver,
f'jdbc:teradata://192.168.119.128/Database={database}',
[user, password],
["../terajdbc4.jar"])
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute(f"create multiset table {database}.{table} (ID int, Text1 VARCHAR(100), Text2 VARCHAR(100))")
cursor.executemany(f"""
insert into {database}.{table} (ID, Text1, Text2)
values (?, ?, ?)""", pdf.values.tolist())
cursor.close()
conn.close()
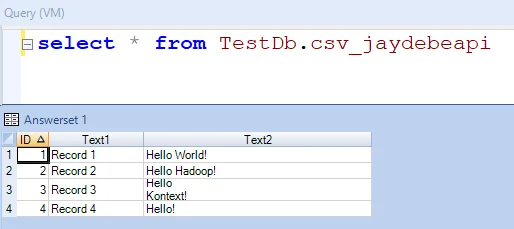
Verify result
The result can be queried directly using Teradata SQL Assistant:
Approach 2 - sqlalchemy
Another approach is to use sqlalchemyconnection and then use pandas.DataFrame.to_sqlfunction to save the result. With this approach, we don't need to create the table in advance.
Create pandas data frame
Pandas data frame can be easily created using read_csv API:
import pandas as pd
file_path = 'data.csv'
pdf = pd.read_csv(file_path)
Save to Teradata
We can use to_sql function of Pandas dataframe to save the data to Teradata.
Definition of to\_sql
The following parameters are supported in the latest stable release (as at 2020-05-03).
def to_sql(
self,
name: str,
con,
schema=None,
if_exists: str = "fail",
index: bool_t = True,
index_label=None,
chunksize=None,
dtype=None,
method=None,
)
Code snippet
The following code snippets create a database engine using connection string. Teradata native ODBC driver is used. You can also add many other connection string parameters for Teradata. sqlalchemy.engine.url.URL can be used to establish a connection too. Parameter query can be used to pass parameters.
For example, the following one use extra parameters (LDAP used as authentication mechanism) when establishing connection.
url = sqlalchemy.engine.url.URL(drivername='teradata',username=user,
password=password,
host=host,
database=database,
query={'authentication':'LDAP','driver':'Teradata','Session Mode':'ANSI'}
)
td_engine = create_engine(url)
Once connection is established, to_sql function is directly invoked to write the data into database. If the table exists already, it will be overwritten since if_exists parameter is specified as 'replace'.
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
import pandas as pd
file_path = 'data.csv'
pdf = pd.read_csv(file_path)
database = "TestDb"
table = "csv_sqlalchemy"
user = "dbc"
password = "dbc"
host = '192.168.119.128'
td_engine = create_engine(
f'teradata://{user}:{password}@{host}/?database={database}&driver=Teradata Database ODBC Driver 16.10')
conn = td_engine.connect()
pdf.to_sql(name=table, con=conn, index=False, if_exists='replace')
conn.close()
Verify result
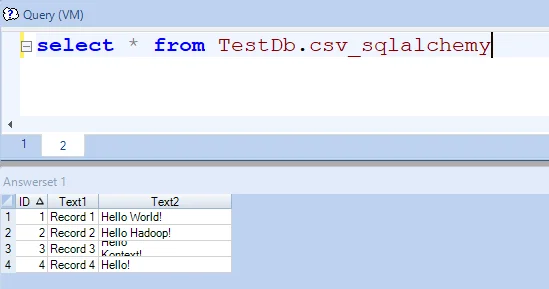
Run the following command in SQL Assistant, it will returns the following result:
select * from TestDb.csv_sqlalchemy